Not just an exchange, what is a crypto exchange?
This article will explain crypto exchange business, how it works, why it’s like this today, pros and cons, in a way that can be comparable to participants in traditional finance market.

Follow us
Author: Phil Yang, Head of BD
Background
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets like BTC and ETH are based on decentralized blockchain ledger technology. However, the crypto trading market mainly happens in centralized exchanges like Binance or Coinbase, which is based on centralized ledger like any exchange / broker in traditional finance.
Despite the similarity of centralization, there are some interesting differences between crypto exchanges (like Binance, and Coinbase) and traditional exchanges (like Nasdaq, and CME), including but not limited to
- Crypto traders are directly using exchanges (onboard, KYC, deposit fund…) to trade, but when trading stocks, traders have to trade via brokers or dealers like Robinhood and IBKR instead of exchanges like NYSE and Nasdaq
- Crypto exchanges are operational 7*24 non-stop (with very occasional maintenance), while stock market has daily open and close hours and no trading on weekends/holidays
With the sudden collapse of FTX, it's meaningful for everyone to understand what caused those differences? What’s good or bad about those difference?
This article will explain crypto exchange business, how it works, why it’s like this today, pros and cons, in a way that can be comparable to participants in traditional finance market (while nothing about how to apply decentralized ledger technology to stock clearing and settlement, or decentralized finance DeFi applications).
TL;DR
- Crypto exchanges cover the service of banks, brokers, prime brokers, asset manager / funds, even VC and payment, on top of traditional exchange services (matching, clearing).
- Limited by cryptocurrency and digital asset market size, even the largest crypto exchanges like Binance or Coinbase are comparable to median-sized traditional finance institutions.
- Crypto exchanges provide all services because of max efficiency, confidence from users, and low level of regulations.
- The nature of global trading and decentralized organization structure makes regulators hard to find a way to regulate global crypto exchanges. However effective regulations have been set in some local markets like Japan.
- In a foreseeable future (likely in 2-3 years), regulators will find ways to regulate global crypto exchanges to minimize counterparty risk, likely by splitting the business of exchanging and settlement. It’s a challenge for crypto exchanges to keep current service level with potential new clearing process.
Before Crypto, How Stocks Are Traded and Settled in Traditional Markets (“Tradfi”)
General Process
How a buyer and a seller trade stocks with each other
- Traders (buyer and seller) store their fund in custody
Custody is either bank or broker (or some banks like HSBC or Standard Chartered also have broker license), where buyer and seller can be using different custody - Traders see market price in brokers / dealers and send trading order to brokers
Where buyer and seller might be using different brokers / dealers - Brokers / dealers will check available fund and freeze the amount
Some brokers / dealers provide financing solutions like prime brokerage to hedge funds - Broker / dealers then send those orders to the exchange for matching buyers and sellers
Buyer and seller will be only matched in the same exchange - After trading, clearing house affiliated to the Exchange will calculate payables and receivables of each membership firm
But the clearing house will settle with only clearing membership firms (some brokers / dealers are the direct clearing members of exchanges, but some are not - If the brokers / dealers are not clearing member of exchanges, they have to work with a clearing membership firm for clearing and settlement
Depending on jurisdiction this process might differ, and there might be difference or additional complication if that’s derivatives trading, or qualified foreign institutional investor with cross-jurisdiction operations

The clearing and settlement process is exchange – clearing member – non-clearing member – retail traders. For more details, traditional exchanges like Eurex publicly announce different types of clearing members.
Now we know to trade stocks, traders will use bank / broker (custodial or non-custodial, clearing and non-clearing members of exchanges) and exchange’s services. If we take a closer look at exchanges, what else do exchanges provide besides matching trades, and clearing?
What Is the Role of Traditional Exchange?
Let’s take Deutsche Börse Group https://www.deutsche-boerse.com/dbg-en/ as an example, which is considered as a full features exchange in traditional markets.

* Multiple trading venues for different instruments and traders in Deutsche Börse Group

In Crypto Market, What Do Crypto Exchanges Do?
Crypto traders can do everything in crypto exchanges. Crypto exchange is the one-station shop to every retail trader or institutional trader that covers bank, broker and exchange’s services.
What's Similar to Traditional Exchanges
This article will mainly use Binance as an example, to compare what’s similar to traditional exchanges. Why Binance - just Binance is the largest in size and also quite complete in business, compared to largest regulated exchange Coinbase, and largest options exchange Deribit.
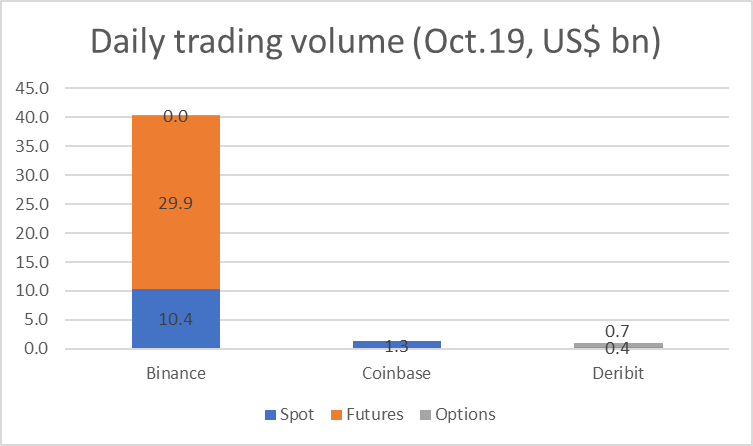

How big is Binance compared to traditional exchanges? Let's compare daily trading volume between Binance and HKEX (was going to use CME as the largest derivatives market as Binance is also the largest crypto derivatives trading venue, but Binance’s volume is a tiny <0.2% fraction compared to CME, so here taking HKEX as a comparable benchmark)
Remember when we say daily volume, it’s a 24-hour volume on Binance while one trading day’s volume for HKEX. Also, Binance trading is live on weekends, while HKEX does not open on weekends.

As a crypto exchange, Binance almost covers every business of Deutsche Börse Group, with some difference.

Custody / Depository
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets are based on blockchain, so deposit and withdrawals are through hot wallet, and finally deposit into exchange’s cold wallet.
There are, however, cash trading which involves banks, e.g., USD, JPY... those are stored in traditional bank accounts under exchanges’ entities. Unregulated exchanges, when handling fiat, usually use shell companies, like FTX use North Dimension Inc., and Binance use Key Vision Development Limited Office, which looks completely unrelated to crypto exchanges.
Listing
Crypto exchanges list both spot and derivatives, where derivatives in crypto can be dated futures, perpetual swap and options. Different instruments have different patterns of listing.
- Spot and perpetual swap, there are new listing and delisting regularly, can be new IEO listings (like IPO in traditional market), or listing of a listed coin (like secondary listing in traditional market)
- Dated futures and options are limited to the largest cap coins (BTC, ETH), and listings are mainly to renew further dates

Frequency of new listings in crypto exchanges is lower than traditional markets.
On equity / coin market, Binance and HKEX. By Jan.-Oct. 2022, HKEX listed 62 new stocks, while Binance 23 new coins. In 2021 same period Jan.-Oct., this figure is 76 for HKEX and 65 for Binance.
General reason is that crypto market is still a much smaller market with less variety of instruments, while crypto market showed obvious seasonality during the bullish 2021 and bearish 2022.
Market Data
In traditional market, exchange data (live data and historical data) costs. Data can be provided by exchange like ICE, or distributor like Refinitiv, to customers like index issuers, trading firms or brokers, live and historical, in L1/L2 that differs in the content and hence price. So public users usually see a market price that is delayed by 15 minutes.
In crypto market, all exchanges provide free market data to all users, live and historical, on trading GUI or by API.


However, the free data’s scope is limited, e.g., no order book data from Binance, so quant trading firms still tend to fetch and keep their own historical data (it’s basic input for their strategy’s back testing). Or there are 3rd party vendors providing crypto market data like 1Token, Lukka and Kaiko.
Matching, Clearing and Settlement
Crypto exchanges conduct matching, clearing and settlement of trades in real-time. Every coin bought can be instantly shown in the balance, available for trading or transfer. This is possible because the broker, exchange, clearing and custody are all provided by one company with close tech integration.
Why can not this be done in traditional markets
- The process clearing and settlement (delivery and payment) process takes exchange – clearing member – non-clearing member – retail traders, so there’s 1) physical asset movement 2) reconciliations for error checking, so each party will need time to finish their work making stock settlement T+1 or even T+2
- Those companies have working hours and working days that do not process trades in holidays, e.g., banking hours on banking days
Advanced Clearing Feature - Portfolio Margin
Both traditional exchanges, and crypto exchanges implement margin requirement based on risk rather than position, for maximizing collateral efficiency of market participants.
In the traditional market, this can be named differently. There are CME SPAN (also used by Nasdaq), and Eurex Plasma, both for calculating margin requirements on futures and options.
In crypto market, exchanges also trade derivatives like futures, options besides spot. OKX and FTX are the early adopters of portfolio margin, and Binance portfolio margin has been production testing with limited user base since Q2 2022 and expects full launch in year 2023.

Collateral and Liquidity Management
Like traditional exchanges, crypto exchanges also serve as 3rd party clearing house for OTC trade. (Binance do not offer this yet, so here we take Deribit as example called Block trades, where institutional trading network Paradigm is the main user https://www.paradigm.co/help/products/derivatives/venues/deribit)

What Else Do Crypto Exchanges Do - Full-Service Financial Services From Bank to Broker
On top of all above exchange functions, Binance additionally plays the role of bank (retail banking, borrowing / lending, asset management), plus broker (retail introduction, institutional prime services, clearing broker and non-clearing broker), plus funds (ETF issuer), and other emerging business.
How big is Binance compared to a real bank – let’s compared total client deposits and balances between Binance and DBS Bank (Binance is a tiny fraction compared to large international banks like HSBC or JP Morgan, so we take DBS Bank which is one of the largest Singaporean banks with operations mainly in Asia).

The fact that Binance as one of the largest crypto exchanges (bank), deposits is ~20% of a top regional bank, is because the crypto market size compared to the whole global finance market is simply much smaller.
Bank
Crypt exchanges are recognized and used as banks. Most retail users and active trading firms park all their fund in exchanges, some cautious long-term holders might use custody service or cold wallet.
Crypto exchanges enable users to withdraw available cryptocurrencies any time (no limit to banking hours or cryptocurrencies).

More fund deposit means bigger potential trading volume, so exchanges trying to keep users’ fund under custody, by deriving various financial services that could be offered by banks or brokers in traditional finance.
Earn
The yield comes from various sources, which could be
- Borrowing positions from margin trading in the exchange, or VIP loans to institutions
- DeFi staking
- Structured earn products backed by options
- Automatic investment plan
Not seen in Binance, but seen from other unregulated exchanges, there can be copy trading to an exchange KOL, variable income investment to external fund manager, or even cash pooling that is not matched with specific assets, but exchanges freely allocate investment on their treasury.

OTC Trading

Broker
Unlike traditional exchanges which only face a limited number of members (brokers usually). Crypto exchanges take the job of brokers, and directly onboard all individual traders and let them trade on web, mobile App and API, with free market data screen, post various types of order (market, limit, trigger, TWAP…), and provide history log.
Here’s Binance spot trading on web GUI (Binance also have futures and options)

Exchanges enable users to participate IEO, which is a similar activity like subscribing new listed stock shares.

Prime Services
Crypto exchanges offer financing by margin trading to all users, or bespoke financing facilities (https://www.binance.com/en/loan/vip) to institutions like prime brokers in traditional market.

Fund / Asset Manager
Binance issues own ETF products like https://www.binance.com/en/futures/DEFI_USDT

Others (Research, Venture Capital, Payment…)
To make good listings, exchanges need research https://research.binance.com/ to keep up with market.
Based on the research, plus capital and access to market, and most importantly listing opportunities, exchanges make VC investment often named labs, e.g., https://labs.binance.com/. Similarly in traditional market, Nasdaq also makes VC investment https://www.nasdaq.com/nasdaq-ventures.
Also Binance aims to be a VISA https://pay.binance.com/en
As those are not core business of exchanges or financial services today, we will not deep dive into those.
To Summarize, Binance Is Acting As an Aggregation of
- HKEX, exchange with listing, market data, clearing
- DBS Bank, bank, asset management and securities brokerage with clearing membership
- Interactive brokers, derivatives broker
- Goldman Sachs, prime broker
- Blackrock, ETF issuer
- Additionally, exchanges might explore below business
- Goldman Sachs, equity research
- Sequoia, VC
- VISA, payment
Why Are Users Fine With Exchanges Today?
Max Efficiency
Trader only to sign up accounts for crypto exchanges, to access all kind of crypto financial services (custody, trading, asset management, financial services…).
Users can trade any listed instruments 7*24 and withdraw holdings immediately after a trade, because crypto exchanges have no dependence on external counterparties, no operational bottleneck for 7*24 hours operations, and real-time clearing settlement.
The current superior user experience already sets the standard for all users, and will be hard for most of them to switch to stock or FX fixed trading hours model.
Tech Advantage
Traditional exchanges are designed for max. several hundred membership firms, and built on technology decades ago.
While crypto exchanges are built in the recent years (Binance is launched in 2017) with modern technology and cloud computing infra with the concept of serving millions of global traders directly.
Low Level of Regulation
Crypto trading is a global market from day 1 and crypto exchanges are operating globally, in two dimensions
- They serve global customers, so Turkish clients can be trading with Brazilian clients. Should Turkey or Brazil authority regulate this trade, and how should they agree on a framework to clear and settle those trade if that has to be an independent 3rd party other than the exchange itself?
- There is not a headquarter for most exchanges. Coinbase as fully licensed exchanges has a headquarter. But for unregulated global exchanges like Binance and OKX, the organization is distributed in several countries
Hence, regulators of any single jurisdiction cannot impose any effective regulations to crypto exchanges.
Only exchanges that have clear local operations, can be regulated by local authorities. Japan FSA did a great job in freezing FTX Japan asset as very first reaction to protect local users. The premise of such effective regulation is that all Japan licensed exchanges such as Bitbank, Bitflyer, Coincheck are operated in Japan, and serving clients in Japan.
Confidence from users
It’s not accurate to say it is simply too big to fail, because we see FTX as the 2nd largest exchange busted in a week.
But users have high confidence to top exchanges like Binance (and FTX, sadly) to take custody of own fund, because they
- proven to be robust in security, that kept fund unhacked, and multi-sig among several people around the world
- retained huge earnings from years of operations, and they capture all the earnings as everything is under one roof
Also, there’s constant twitter posts from CZ openly discussing with users, and market Binance SAFU program (Secure Asset Fund for Users) which now exceeds US$1 billion.
The Risks Behind
Risks is mainly the counterparty risk, to crypto exchanges and blockchain. Every year there are crypto exchanges down, due to recklessness or simply fraud, as a result the depositors cannot have their fund back. In 2022, even FTX the 2nd largest exchange in crypto market failed, where they have a US$ 10-50 billion hole on balance sheet… and FTX will not be the last.
Why is that?
Low Transparency
Crypto exchanges are not transparent. Even they published their wallet address and hence assets like https://portfolio.nansen.ai/entities, only few people from inner circle can know the real situation.
As the former FTX Head of Institutional Sales writes, foremost I would like to make it abundantly clear that the VIP team was left completely in the dark and were in no way aware that FTX was insolvent or that customer assets were at any point not backed 1:1.
Internal Control on Decentralized Organization
With FTX filing for Chapter 11, people get to know how bad their internal control is.
I’m sure most crypto exchanges try to impose effective internal control for shareholders’ interest. But it’s a realistic challenge to make effective finance controlling, since most exchanges are operated with decentralized organization.
Using Client Deposits
There are Earn programs which users grant the exchange rights to use their funds, here I’m talking about the fund users think as a ‘deposit’ that sits in spot balance not ‘earn’.
For conservative exchanges, they put minor portion into almost-risk-free yield of 4-5% from bank deposit yield or DeFi staking yield.
For aggressive exchanges, they invest into a wide scope of secondary market trading, lending / borrowing in the public market, equity or token investments… which is expected to generate higher yield along with higher risk.
It’s no secret that many exchanges have internal market making desk to provide liquidity to own users (like FTX-Alameda), where does the trading principal come from and what happens if there’s a loss?
Regulation
In traditional finance market to enable cross-jurisdiction trading, there has to be a framework among exchange, member, system provider, broker and custody to make sure there’s a way to split responsibilities and claw back potential errors.
To crypto exchange with global operations, none of the authorities could effectively make any regulation, except that in 2020, US CFTC charged BitMEX exchange because BitMEX as a derivatives exchange had served US users.
Today, top unregulated global exchanges like Binance, OKX have learnt the lesson from BitMEX by strictly banning all US users from their international exchange, and migrating US users to their US website Binance.US and OK Coin.
If you combine above 4 points, that makes FTX – aggressively using client deposits, poor internal control (high expense), low transparency (unaware of the huge loss) and absence of regulation.
Additionally, there’s technical money laundering on blockchain via Tornado Cash protocol, making laundered fund untraceable any more.
Emerging Trend and Outlook
There are both bottom-up and top-down measures, driven by regulators or technology. I have no doubt that investors and traders will have better protection, however the main issue is how to keep current service level (7*24 market, real-time clearing settlement…) after implementing those measures.
Here is some potential outlook
Business Architect – Split Custody and Exchange Business
- Exchange splitting custody business
Like US Gemini has
https://www.gemini.com/custody
https://www.gemini.com/clearing
https://www.gemini.com/exchange
(Binance and Coinbase also have similar moves of splitting) - Independent 3rd party custody acting as clearing member
Copper or Etana’s asset in the trading wallet will be recognized by Binance, Kraken… and will be settled between custody and exchange regularly
This is like the process in traditional finance market, that custodian / clearing member is independent to broker and exchange. - Self-custody solution that integrates with exchange
Leading self-custody solution Fireblocks could be highly integrated with exchanges in the future.
Effective Regulations
US regulators, such as SEC and CFTC with long arm jurisdiction rights, might be the global rule maker to regulate crypto market.
There has been news around CFTC’s Digital Commodities Consumer Protection Act (DCCPA), a proposed United States federal law to regulate the trading of cryptocurrencies and related digital asset. As the former FTX CEO Sam Bankman-Fried was one of the advocators who’s lobbying Congress, the recent collapse of FTX might trigger further modifications and delaying the timeline of enacting the DCCPA.
Nevertheless, if the market size of cryptocurrency and digital asset market keeps growing substantially, global regulators will have to agree on an effective way.
Both Commercial and Technical Auditing
FTX claimed that its 2021 financial results had been audited by Armanino, one of the 20 largest accounting firms in the country by revenue.
After FTX collapse, exchanges all prove asset by technical ways like Merkle trees or showing wallet address. Vitalik who created Ethereum also published new ideas https://hackmd.io/@vbuterin/proof_of_solvency
However, due to the complexity of cryptocurrency and digital assets market, even top accounting firms might not fully understand the business mode or not equipped with the right technical tool to conduct effective auditing.
DeFi
Different protocols built on blockchain smart contracts for different purpose. E.g., AAVE and Compound for saving and borrowing, Curve for stablecoin trading, Uniswap V3 for spot trading, dYdX for perpetual trading
With Blockchain as the clearing and settlement layer, DeFi brings transparency to users, though there's technology risk and hacking risk.
1Token Introduction
This article is from 1Token, crypto native technology provider since 2015.
1Token offers one-stop tech solution for crypto-financial institutions, that are
For various financial service lines –
Buy-side: fund, asset manager, FoF, treasury, VC
Sell-side: lending, PB, OTC, custody
3rd party: fund admin, auditing firm
Supporting key functions –
Front-office: sales and trading, trade execution
Middle-office: operations, portfolio and risk control
Back-office: clearing and settlement, finance and treasury, trade reconciliation
Covering all web3 assets –
CeFi spot and derivatives (perps, futures, options, traded in Exchanges or OTC)
Others like loan, DeFi, SAFT, mining…
Integrated to all venues –
Exchanges, OTC, Custody, DeFi protocols
1Token software is used by 40+ large institutions globally, with top names like Amber, Antalpha, LTP, Matrixport, Nexo, and top exchanges
With full coverage on cryptocurrency and digital assets, 1Token implements treasury monitoring for large complex institutions, and asset/ transaction recording/ analysis for crypto auditing teams.
Financial institutions that have multiple BU or entities, can be assigned different exchange accounts or blockchain address, and record internal loans with internal interest rate. So that the CEO/ CFO / treasurer can have the transparency of assets and liabilities, period PnL of the whole company, and by each BU or entity.
Sources
https://www.deutsche-boerse.com/dbg-en/
https://investors.interactivebrokers.com/ir/main.php?file=latestMetricPR









Comments ()